The world of animation is vast and infinite. Countless wonders are found within it. Anything that is possible in live-action media, can be translated into animation as well. And things that would never work in live-action - such things tend to work surprisingly well when animated. It seems this technique truly has no limits.
There is only one downside: animation is not easy to produce. If you ever tried to animate anything, you know that even the simplest of motions require quite a bit of effort and a surprising amount of time.
Because of this, people have always sought for ways to simplify the process of creating animation, to make it faster and more efficient - but not by sacrificing quality and artistry. In older times, this was mostly achieved through various types of rotoscoping - basically using live-action footage as a basis for drawings - but modern animation is mostly done on computers. So it is logical that computers also became the means for making animators' lives better.
After all, computers are known for being able to make things that can very well appear magical for an outside viewer. In fact, there was once an urban legend that some cartoons are made by feeding a computer a number of sketches and a script, with the machine doing the rest.
That rumor was obviously not true - nor could it have been in that day and age, as computers back then simply were not powerful enough to pull off something like this.
But as technology continues to move forward, new horizons continue to open before us. Dramatic increases in computation power mean that methods and algorithms that were not viable before can be put to use now. Things that were not possible me years ago become reality today.

Here, for example, we have a picturesque landscape created entirely by a computer. The system goes through thousands of pre-existing landscapes - photographs or paintings - to determine how they are constructed, and then it is able to construct landscapes of its own.
Things like this came to be known as artificial intelligence. Nowadays, this is the frontier of computer science, and discoveries made on this frontier are widely used for all manner of purposes: scientific, technical, artistic - with this latter one being most interesting to us.
In this article, we'll be looking at how artificial intelligence can be applied to various tasks an animator - and specifically a 3D animator - could face.
Historically, one of the first cases of using AI to do animation work was simulating crowds.
Crowds were always tricky to animate: simply copying one animation would easily betray the artificial nature of such a 'crowd', while animating each member individually would require enormous effort.

This is how crowds were animated at the time. This method works well enough if the crowd consists of some robots or such, but it's hardly fitting for living creatures.
In time, bright minds at CG studious invented a way to circumvent this problem using a system similar to those used in many game engines.
There, a crowd is made of characters - often referred to as 'agents' - that are programmed to perform various tasks such as moving or interacting with each other, all while playing appropriate animations. This way, an animator can bring to life hundreds, even thousands of characters with each one of these characters acting like the others, but not exactly the same. This variety that is so difficult to achieve manually is what brings crowds to life.

An example of a crowd generated by the MASSIVE software; scenes made using this - or similar - software can be found in many modern films.
The first movie to ever do this was the Lord of the Rings (2001 - 2003). Nowadays, this is a well-developed and widely used technique, known for producing impressive results. Many modern 3D software solutions include variants of this technique.
But the AI used in such a technique is rather basic: a simple decision-making system you'd expect to see in a video game. At the time, this was what the words 'artificial intelligence' actually meant - but that's not quite the case nowadays.
As technology advanced, many new solutions and approaches were either developed from the ground up or became viable to use with modern equipment. Currently, the very words 'artificial intelligence' are not so much a designation for a particular technology as they are an umbrella term for a variety of systems and techniques. And easily the most prominent of these techniques is machine learning.
This method operates by taking a large number of examples - be it images, animation data or anything else - and using neural networks to analyze these examples, and to find what they have in common: a set of 'rules' that would be common for all this information. This process is known as training; it is slow, it is computation-intensive, and it requires a lot of information prepared in a specific way beforehand - but it only has to be done once. And when it is complete, the fully-trained network can use the rules it devised to generate data of its own: similar to that in the examples it was trained on, but by no means the same.
We've already seen what this approach is capable of: this is how the landscape above was created. And this is how more and more things are created nowadays.
Neural networks are widely used in various fields of computer graphics, including 3D animation. And one of the examples would be the case of motion matching.
Motion matching refers to a clever way of partially automating character animation. Basically, such a system takes a big set of various animations (hand-made or motion captured) and the character input data such as velocity and direction, type of terrain, objects in the scene, user input and so on. The system then analyzes this input data to determine which animation clip from the library best suits the current circumstances.
The process is repeated continuously, often several times in a second. The animations it picks are combined together and smoothed to create a seamless, continuous motion.
An approach like this eliminates a lot of manual work from the process of animation, and it is known to produce good-looking results. But it also comes with its own set of problems: it is somewhat heavy on the performance, and it takes a lot of memory to store all these animations.
To combat these shortcomings, a variant of this technique - Learned Motion Matching - was invented. It works in a similar way, but doesn't use the animation library. At least not in runtime: this library is instead used to train a neural network to generate poses and animations fitting for the given input data - and it is this network that is then put to use in the application itself.
This approach significantly reduces the memory usage, - sometimes by orders of magnitude! - as well as the impact on performance. Moreover, when set up properly, animations produced by it are almost identical to the ones in the library.
Such is the power of machine learning. But while this is indeed an impressive achievement, this approach still relies on pre-defined sets of animations.Which raises the question: is there a way to use AI to actually create animations, or at the very least to simplify this process?
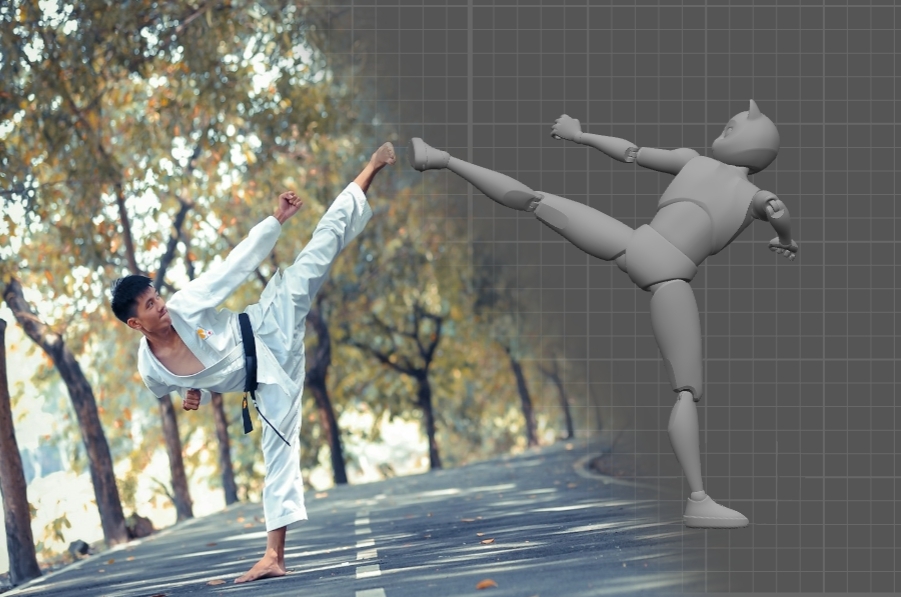
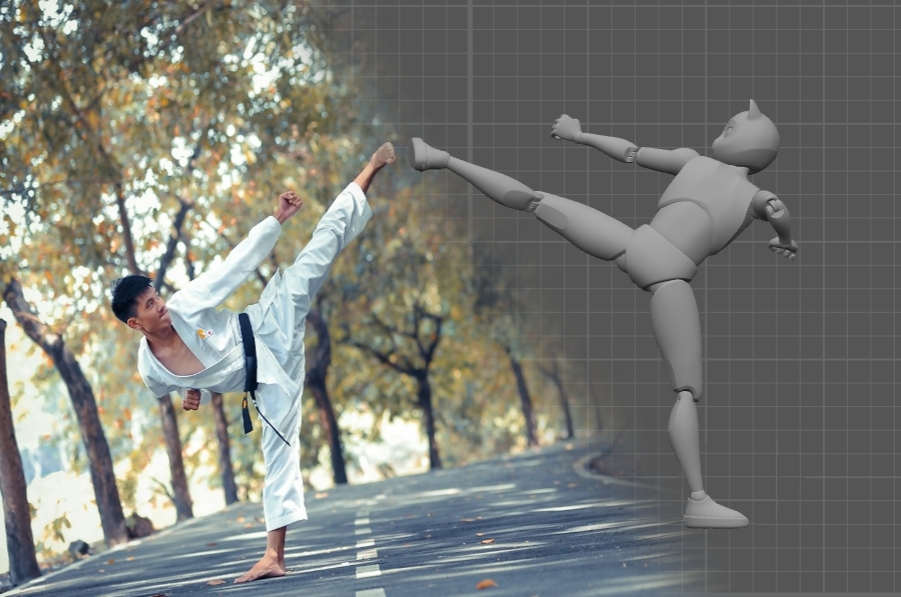
Over the years, there were numerous attempts to do this. One of the approaches is using AI to 'copy' poses from a reference and apply them to a 3D character. In a way, this is a modern variant of the old rotoscoping technique. It is widely used in animation, but the process is tedious, time-consuming and nobody wants to do this - and thus it seems natural to try and automate it.

Clip Studio Paint, a well-konw painting software, has a feature to turn a pose from a photo into a reference for drawing.
This feature is relatively new, but it is already used in production. Variants of it can be found in some 2D painting software solutions, where it is used for sketching and building composition, and there are several implementations for 3D animation as well. It has its limitations - for example, it doesn't seem to be able to handle several characters at once - but in the right hands it is a powerful tool that can greatly cut the time you spend on setting up poses and motions for your characters .

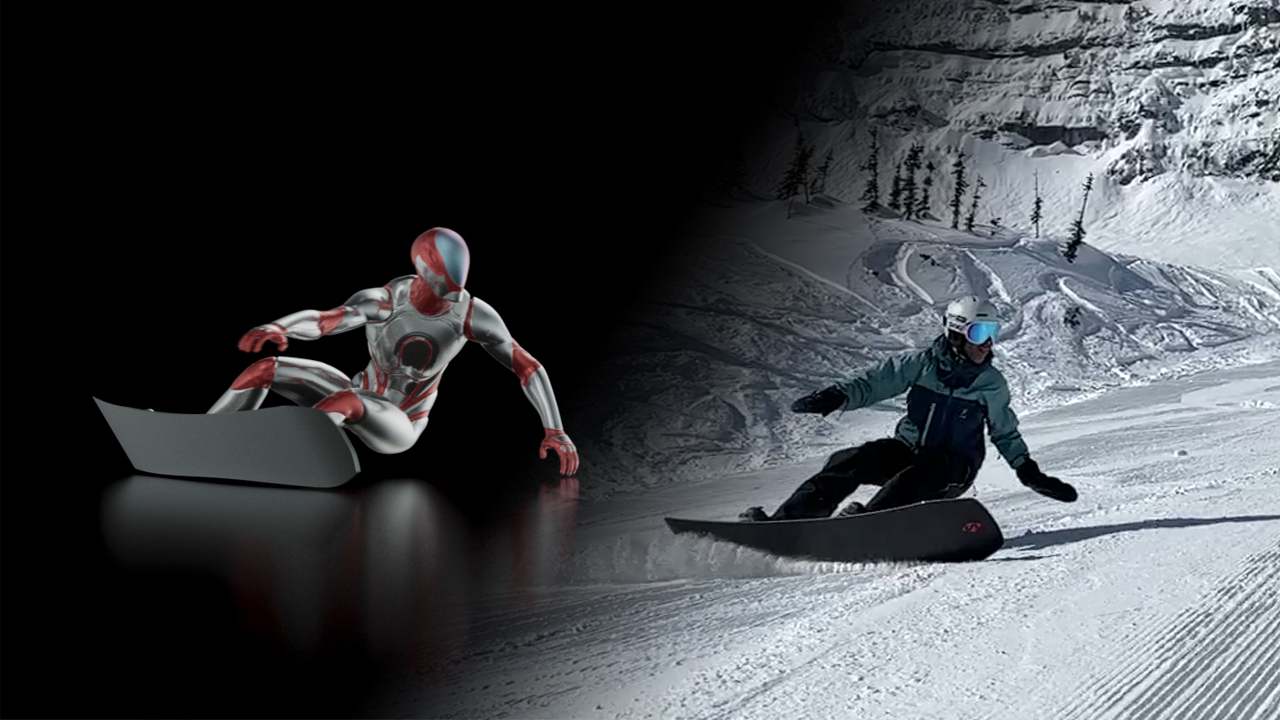
In a similar way, the RADiCAL solution uses video sequences to generate 3D animations.
A different - and more complicated - approach would be to use AI for generating animation from scratch.
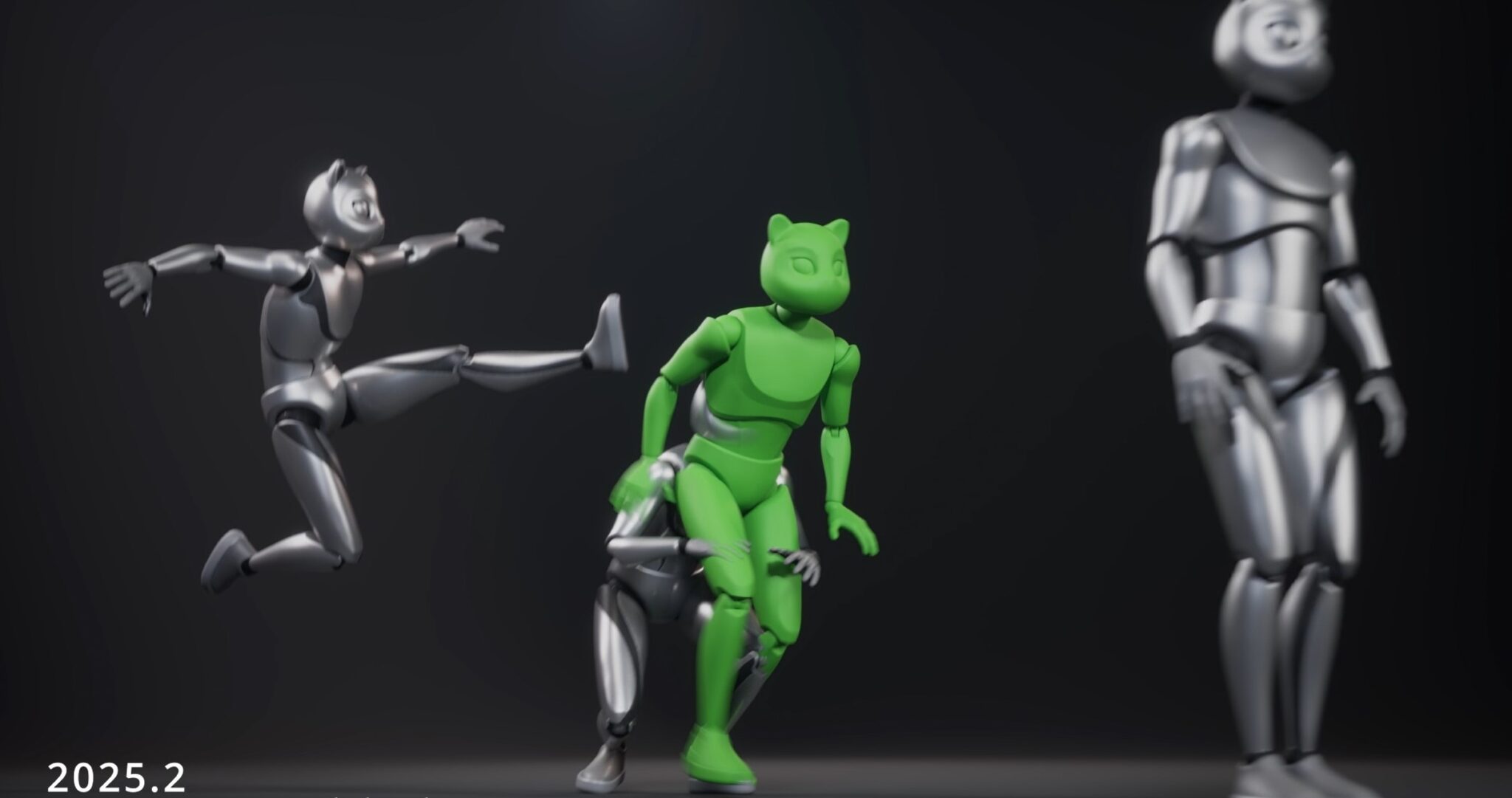
One of the ways AI can be used to generate actual animation without using references.
Here, an AI system is used to 'train' a 3D character to perform various motions. After training is complete, the character can combine these motions in a variety of ways to move around, interact with objects and generally perform tasks the artist sets for them.
Once again, this is similar to controlling a video game character - only this character reacts to the user's commands in a much more complex and nuanced way.
But while generating animation out of the whole cloth is certainly an impressive achievement, a tool like this might not be what an animator would prefer to use in their workflow.
The classical animation process is based on full control over the character, an approach that is not really compatible with said characters making their own decisions, even within user-defined goals.
On the other hand, said decisions do sometimes produce unexpectedly interesting results, and, as shown by the examples above, AI-based tools are a great way to get rid of the treadmill work that to this day plagues the process of animation.
So the question arises: is there a way to have the best of both worlds? Could there be an animation tool that gives you means to directly control the character, while using AI to automate all those secondary tasks that you are traditionally expected to do with your two hands?
The answer would be: …sort of.
Nekki's animation software Cascadeur does include a somewhat similar feature:
Much like in all the previous examples, this solution uses a neural network trained with data from hundreds of short animation clips. The difference, however, is that this time AI is used in conjunction with user input.
As you can see, the character here has several points attached to various body parts. When the user moves one of these points, the corresponding body part moves along with it. But this is not all: the system tries to predict which pose the user aims at - and accordingly moves the rest of the body. An approach like this does not solve all the problems. The quality of poses generated by the tool can be uneven sometimes. And other times the software might suggest a pose completely unlike what you have in mind - because, of course, it has no way of knowing exactly what you do have in mind. But even still, it makes setting up complex poses quite a bit easier than it would be with more traditional tools. Using AutoPosing is a great way to quickly set up a rough draft for your animation.

The AutoPosing feature in Cascadeur can quickly generate a huge variety of poses that can be subsequently used for laying out the animation.
And with this, our little overview of AI in character animation comes to an end. This list is by no means complete, - there are other cases worth talking about - nor is it set in stone.
The technologies behind artificial intelligence continue to grow rapidly, and what this means is that existing solutions will continue to improve, and there will most certainly be new discoveries.
But what will become of these discoveries, only time will tell. Maybe there will be fully automated animation tools that will eventually bring that old urban legend to life. Or maybe the focus will shift from AI-based to AI-assisted tools that make the animator's work easier and more convenient without doing it in their place..
What is for sure, though, is that this field will continue to grow day by day , technologies will keep moving forward, and even more new tools and techniques will arrive to further optimize the ever-challenging process of crafting good-looking animation.
And we here at Cascadeur team too will continue our work of refining our own tools as well as introducing new ones, so if you have any thoughts, feel free to share them in the comments. And stay tuned - the world of animation still has many topics worth talking about.
Addendum notice:
Developers from the custom AI development services provider Azumo state , 'We view artificial intelligence as a transformative force in animation. By harnessing AI's capabilities, creators can automate labor-intensive processes such as in-betweening, character rigging, and real-time rendering, significantly accelerating production timelines. AI-driven tools, like neural networks, enable adaptive animation that reacts dynamically to user inputs, opening up new possibilities for interactive storytelling and gaming. Furthermore, generative AI models can create stunning visual effects and even conceptualize unique art styles, pushing the boundaries of creative expression. AI in animation is not just about efficiency; it's about empowering artists to bring imaginative worlds to life in ways previously thought impossible."








